Understanding and Managing Long COVID Symptoms
Navigating Long COVID Symptoms. As the world continues to recover from the acute phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, many individuals face a lingering challenge: Long COVID. This condition refers to a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or even months after the initial infection has cleared. Navigating these symptoms can be confusing and frustrating, but understanding what Long COVID entails and how to manage it can help improve quality of life.
What Is Long COVID?
Navigating Long COVID Symptoms also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), affects a significant number of people who have had COVID-19, regardless of the severity of their initial illness. While most recover within a few weeks, others experience ongoing symptoms that can disrupt daily life.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
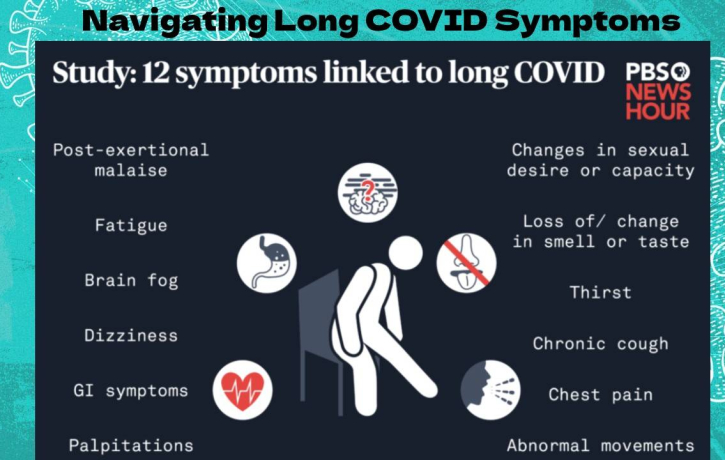
Long COVID symptoms vary widely but often include:
-
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
-
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless with minimal activity.
-
Cognitive Issues: Often called “brain fog,” this includes trouble concentrating, memory problems, and confusion.
-
Muscle and Joint Pain: Ongoing aches or stiffness.
-
Chest Pain and Heart Palpitations: Irregular heartbeat or chest discomfort.
-
Sleep Disturbances: Trouble falling or staying asleep.
-
Anxiety and Depression: Mental health challenges linked to prolonged illness.
Why Does Long COVID Happen?
Navigating Long COVID Symptoms. Researchers are still uncovering the exact causes, but potential explanations include persistent inflammation, immune system dysregulation, and lingering viral fragments in the body. Some theories also suggest that COVID-19 may trigger or worsen other underlying health conditions.
How to Manage Long COVID Symptoms
Managing Long COVID requires a patient and multifaceted approach:
-
Medical Evaluation: Consult healthcare providers who are knowledgeable about Long COVID. They may recommend tests to rule out other conditions and tailor a treatment plan.
-
Symptom Tracking: Keep a daily journal of symptoms, noting their severity and any possible triggers. This can help your care team adjust your treatment effectively.
-
Pacing and Rest: Listen to your body and avoid overexertion. Balancing activity with rest can prevent worsening symptoms.
-
Physical Therapy: Gentle, guided exercise can improve stamina and reduce muscle pain, but it should be introduced gradually.
-
Mental Health Support: Seek counseling or support groups to cope with anxiety, depression, or isolation.
-
Nutrition and Hydration: A balanced diet and adequate fluids support overall health and recovery.
When to Seek Urgent Care
If you experience severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, confusion, or fainting, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Looking Ahead
Long COVID is an evolving medical challenge, but progress is being made. Ongoing research is shedding light on effective treatments, and many healthcare systems are developing specialized clinics to support patients. Patience, self-care, and professional support remain key in navigating this condition.